A NS packet is composed of a stack of headers, and an optional data space (see Figure 12). As briefly mentioned in the "Simple Simulation Example" section, a packet header format is initialized when a Simulator object is created, where a stack of all registered (or possibly useable) headers, such as the common header that is commonly used by any objects as needed, IP header, TCP header, RTP header (UDP uses RTP header) and trace header, is defined, and the offset of each header in the stack is recorded. What this means is that whether or not a specific header is used, a stack composed of all registered headers is created when a packet is allocated by an agent, and a network object can access any header in the stack of a packet it processes using the corresponding offset value.
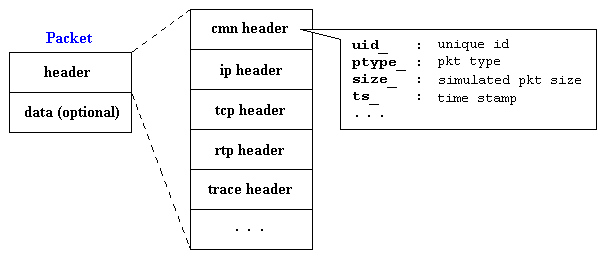
Figure 12. NS Packet Format